|
Cold Lake Veterinary Clinic - Puppy Information
Congratulations on your new puppy! Here is some information to help you get started
The following document highlights all of the resources you may need to support you in your ownership of a young puppy.
The early days of socializing and training are very important to set the stage for your furry-friend experience moving forward.
If you have any questions about any of the topics found here, please call the clinic to speak to one of our staff: 780-594-5212

Puppy Health Topics
Vaccines:
Puppies need a series of vaccine boosters at 8, 12 and 16 weeks. Once a puppy is finished his or her puppy series, they are then vaccinated again yearly thereafter.
Parasites:
Intestinal Parasites: Internal parasites are transmitted from the mother to her pups in her milk and so it is important that puppies have proper deworming after they are adopted. Sometimes a puppy will have signs such as vomiting or diarrhea but most often there is no evidence of a parasitic infection. With a truly severe infection, a puppy can die from intestinal parasites. Your veterinarian will deworm your puppy with each vaccine in the puppy series and may recommend more frequent deworming if needed.
Adult dogs should be also be dewormed regularly to reduce their parasitic burden and to reduce the risk of passing parasitic infections on to people.
External Parasites: Fleas and ticks are a common issue in dogs and can be prevented with the use of preventatives. Please ask your veterinarian about products that are available and when to use them.
Food:
Puppies should be fed a diet that is labelled for growth
- for at least 6 months of age for small breeds
- for 12-18 months of age in large and giant breed dogs
- Large and giant breed dogs should be fed a diet that is labelled for growth in large breed puppies since they have different nutritional requirements than a small breed dog.
Please MEASURE the amount of food that is fed each day rather than free feeding your pet.
- Roughly follow the volume guidelines recommended on the dog food bag until your dog is 12-24 months old.
- Once your dog is mature, feed a volume that helps your dog maintain a good lean body condition.
Nutrition is very important for a growing puppy, so finding a balanced diet is key to their long term growth and health. Any commercial dog or cat food must meet the standards set by the Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO) in North America. These foods will have a label on the bag that says they have either been formulated to meet the nutritional levels of AAFCO or that there are animal feeding tests using AAFCO procedures. The best foods are the ones that have animal feeding tests done on them since these foods have actually been fed to animals and any issues have been corrected.
Companies with good research behind their foods include Purina, Hills, Royal Canin and Iams. It is also important to note that grain free diets are not recommended for dogs as there is a small but significant risk of a heart failure associated with feeding grain free and boutique diets.
Raw and homemade diets are also not recommended because they are often imbalanced and there is a significant risk of infectious disease to the puppy and the owner. Please ask your veterinarian for a referral for a nutritional consultation if you would like to feed a raw or home cooked diet.
Spay and Neuter:
There are many reasons to spay or neuter your pet and your veterinarian would be happy to discuss the pros and cons in more detail.
Spaying: Spaying is removal of the ovaries +/- the uterus in a female dog or cat. Spaying a female dog or cat before she goes through her first cycle helps to drastically reduce her risk of breast cancer later in life to below 1%. If she is spayed after her first heat cycle, her risk of breast cancer goes up to 8% and then up to 26% if she is spayed after her second heat cycle. Spaying your pet also eliminates the risk of ovarian cancer, uterine cancers, unwanted pregnancy, and life-threatening uterine infections.
Neutering: Neutering is removal of the testicles and spermatic cord in a male dog or cat. Neutering helps to reduce behavioral issues such as roaming, fighting, aggression, spraying (in cats) and marking (in dogs) especially if they are neutered before the onset of these behaviors. It also eliminates the risk of testicular cancer, reduces the risk of prostate enlargement and prostatitis. It is a common myth that male dogs will lose their personality after neutering but this is not true.
Teeth:
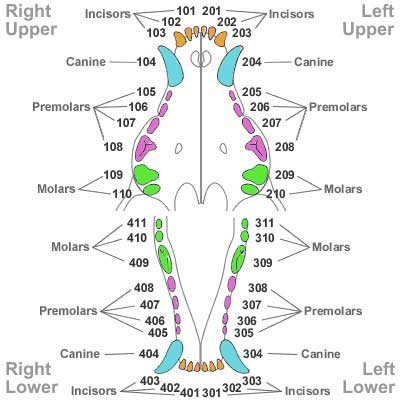
Dental Concerns: Your veterinarian will examine your puppy’s teeth with each puppy visit and will let you know if they see any dental issues that should be addressed.
It is important to remember that some issues cannot be assessed until all or most of the adult teeth are present. At the time of the spay or neuter, your veterinarian will
closely examine the teeth for any issues than can be addressed while under anesthesia. Small breed dogs and brachycephalic (smoosh faced dogs) are especially prone
to dental issues. For more information, please ask your veterinarian.
Insurance:
Pet insurance is a good idea for any new pet owner and can help owners to manage the cost of vet bills if their pet is ever injured or ill. The best time to get pet insurance is when your puppy is young and healthy since your premium will be at its lowest then. If you have questions, please ask your veterinarian. Pet Insurance Comparison Worksheet Pet Insurance Basics
   
Puppy Training Topics
Socialization:
Your puppy is in a critical and sensitive learning stage of their life starting at 6 weeks of age and ending at 16 weeks. Learning through association is happening all the time through each life stage. Whatever your puppy feels emotionally they are relating their their surroundings and environment. So it's important to listen to your puppies body language when socializing them, and make sure they are happy, comfortable and relaxed. Do not overwhelm your puppy during this stage or put them in terrifying experiences. Take your pup on a walk in different neighborhoods a week, take them on field trips and expose them to novel objects. Download our Socialization Checklist to help you set your puppy up for success. If you are nervous about socializing your new puppy read this article!
Toilet Training:
- Routine and Schedule: Set a timer, every hour at first, to bring your puppy to the potty station. You may need to carry or leash your puppy to bring them to their preferred potty station.
- Supervision is Key: You will need to supervise your dog at all times; tethering or confinement tools like a crate and exercise pen will help you keep an eye on your dog and watch for their potty signals. Some puppy's spin around or or sniff as a sign they may need to use the bathroom.
- Reinforcement: When your puppy eliminates outside, it is important to reward them with treats, love or toys (whatever they love the most). It is very common for a puppy to slightly miss the potty area; you will
still want to reward your puppy for any effort around the toilet station to encourage and motivate them.
- Accidents Happen: All accidents are due to lack of supervision or their potty signals were missed. Avoid punishment as this just teaches your pup that's its not safe to eliminate in front of you and instead eliminate when you are not around.
- Management: Managing a situation rather than trying to change your dog’s behavior is sometimes the easiest answer to a behavior problem for both you and your dog. An example of using management is removing precious objects that your puppy might mistake for chew toys. Removing tempting food from the kitchen counter is also a great example of using management. The ma in purpose of crate training your puppy is to prevent them from getting into trouble or harming themselves. It can also be very helpful for the purpose of preventing unwanted behaviors. Examples of management: exercise pen, baby gate, muzzle ,leash, window coverings and crates.
Teething, Mouthing and Chewing:
Teething: A puppy’s adult teeth will all erupt between 3 and 6 months and all the baby teeth will be lost in this time. During this time, puppies will often chew on many things, including things that they are not supposed to. It is essential to have a variety of toys and chews available for puppies at this time to satisfy their need to chew. Most veterinarians recommend that puppies have 1 hard (like a rubber chew), 1 medium and 1 soft toy available at all times so that they are able to choose what they want to chew on. Hard items such as antlers and bones are not recommended because they can cause expensive damage to the teeth in dogs and sometimes can cause intestinal issues. We do not recommend the use of felt type balls and toys such as tennis balls since they cause unnecessary wearing of the teeth.
Chewing: There are many reasons for dogs to chew: self-soothing during teething, boredom, exploring, lack of mental and physical stimulation, separation anxiety or just because a dog is being a dog. Dog’s explore the world around them with their mouths, they don't have thumbs. They use their mouth for investigating new things. Here are some helpful tips to prevent and manage inappropriate chewing in this article.
Mouthing: Puppies explore the world around them using their mouth. This can lead to your puppy mouthing or biting you. It’s really important that your puppy learns to keep their teeth away from human skin. Read this article for some mouthing relief tips.
Jumping:
Its important to create a foundation that is appropriate for you and your dog. Teaching your puppy to greet people calmly now as they are small and young is a great preventative than waiting till your puppy is bigger. For tips on encouraging calmer greeting read this article.
Training Methods:
Positive reinforcement means we are adding something desirable to the learner in order for the behavior to happen more frequently. Dogs are extremely food motivated and especially at this early learning stage a high rate of reinforcement is appropriate for our puppies to learn good habits. Our puppies do not know anything at this stage and its our job to point them in the right direction through reinforcement. Avoid the use of punishment as dogs don't under stand right from wrong. The use of punishment can cause fear, stress and anxiety in our pets but its also in effective. The use of punishment doesn't actually teach our dog what we expect out of them.
Reward all the desirable behaviors that you see as much as possible and ignore the undesirable. If the behavior is undesirable teach them an alternative behavior as a replacement. Count 50 treats into a jar once a day and observe your puppy doing desirable behaviors (sitting, relaxing, offering eye contact, etc) go up to your puppy and reward them, 50x a day. You will find your puppy offering these behavior more frequently. Smart 50x
Myths about Dominance Theory and why it should be avoided: https://avsab.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/Dominance_Position_Statement-download.pdf
Humane Dog Training: https://avsab.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/AVSAB-Humane-Dog-Training-Position-Statement-2021.pdf
How to Hire a Trainer: https://avsab.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/How-to-Choose-a-Trainer-Position-Statement.pdf
Pawsitive Peaks Training & Behaviour
Nail Trimming Resource
Enrichment Explained: Stimulating Your Dogs Mind
Appropriate and Friendly Dog Play
Travelling with Your Dog
| 
